Custom editors attributes
This page lists all common attributes that are used by the Custom Editors pipeline. Each attribute comes up with a short explanation and the usage example.
HideInEditor
Makes a variable not show up in the editor.
[HideInEditor]
public int CoolVariable;
ShowInEditor
Makes a variable show up in the editor even if it's private.
If used on a private field/property you may also need to add SerializeAttribute to ensure that modified value is being serialized.
[ShowInEditor]
private int CoolVariable;
VisibleIf
Shows property/field in the editor only if the specified member has a given value. Can be used to hide properties based on other properties (also private properties). The given member has to be bool type.
public bool ShowIt;
[VisibleIf(nameof(ShowIt)]
public int CoolVariable;
ReadOnly
Makes a variable show up in the editor as read-only (editing is disabled).
[ReadOnly]
public int CoolVariable;
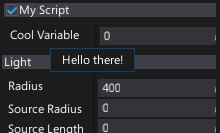
Tooltip
Specifies a tooltip for a property/field in the editor. Useful to provide documentation for object properties.
[Tooltip("Hello there!")]
public int CoolVariable;
Limit
Used to make a float or int variable in a script be restricted to a specific range.
[Limit(0, 100, 0.1f)]
public int CoolVariable;
Range
Used to make a float or int variable in a script be restricted to a specific range. When used, the float or int will be shown as a slider in the editor instead of default number field.
[Range(0, 100)]
public int CoolVariable;

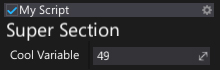
Header
Inserts a header control with a custom text into the editor layout.
[Header("Super Section")]
public int CoolVariable;
Space
Inserts an empty space between controls in the editor.
[Space(50)]
public int CoolVariable;
EditorDisplay
Allows to change item display name or a group in the editor.
[EditorDisplay("My Super Group")]
public int CoolVariable1;
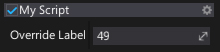
[EditorDisplay(null, "Override Label")]
public int CoolVariable;
EditorOrder
Allows to declare order of the item in the editor. Items are listed from the lowest to the highest order.
[EditorOrder(-10)]
public int CoolVariable;
ExpandGroups
Marks the item to be visible in editor by expanding all the container groups in the upper hierarchy.
[EditorDisplay("My Group"), ExpandGroups]
public int CoolVariable;
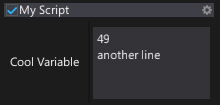
MultilineText
Instructs UI editor to use multiline textbox for editing string property or field.
[MultilineText]
public string CoolVariable;
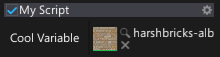
AssetReference
Specifies a options for an asset reference picker in the editor. Allows to customize view or provide custom value assign policy.
[AssetReference(useSmallPicker: true)]
public Texture CoolVariable;
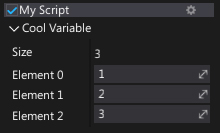
Collection
This attributes provides additional information on a member collection.
[Collection(ReadOnly = true)]
public int[] CoolVariable = new int[]
{
1,
2,
3,
};
Button
Button attribute displays the method as a clickable button in the editor's properties panel.
/// <summary>
/// Button tooltip comes from this comment.
/// </summary>
[Button]
private void CallMe()
{
Debug.LogError("Ho!");
}

CustomEditor
Overrides the default editor provided for the target object/class/field/property. Allows to extend visuals and editing experience of the object.
[CustomEditor(typeof(MyScript))]
public class MyScriptEditor : GenericEditor
{
public override void Initialize(LayoutElementsContainer layout)
{
base.Initialize(layout);
layout.Space(20);
var button = layout.Button("Click me", Color.Green);
button.Button.Clicked += () => Debug.Log("Clicked!");
}
}
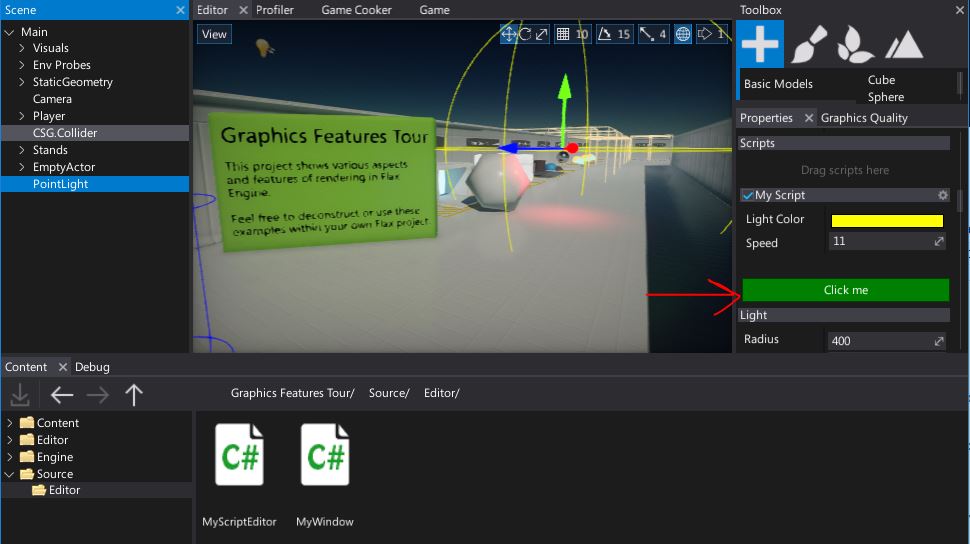
CustomEditorAlias
Works the same as CustomEditor attribute, except uses a typename that can be located in different assembly (not referenced).
[CustomEditorAlias("MyScriptEditor")]
public class MyScript : Script
{
public float Speed = 11;
public Color LightColor = Color.Yellow;
}